开始前的准备
1
2
| $ go get github.com/KenmyZhang/aliyun-communicate
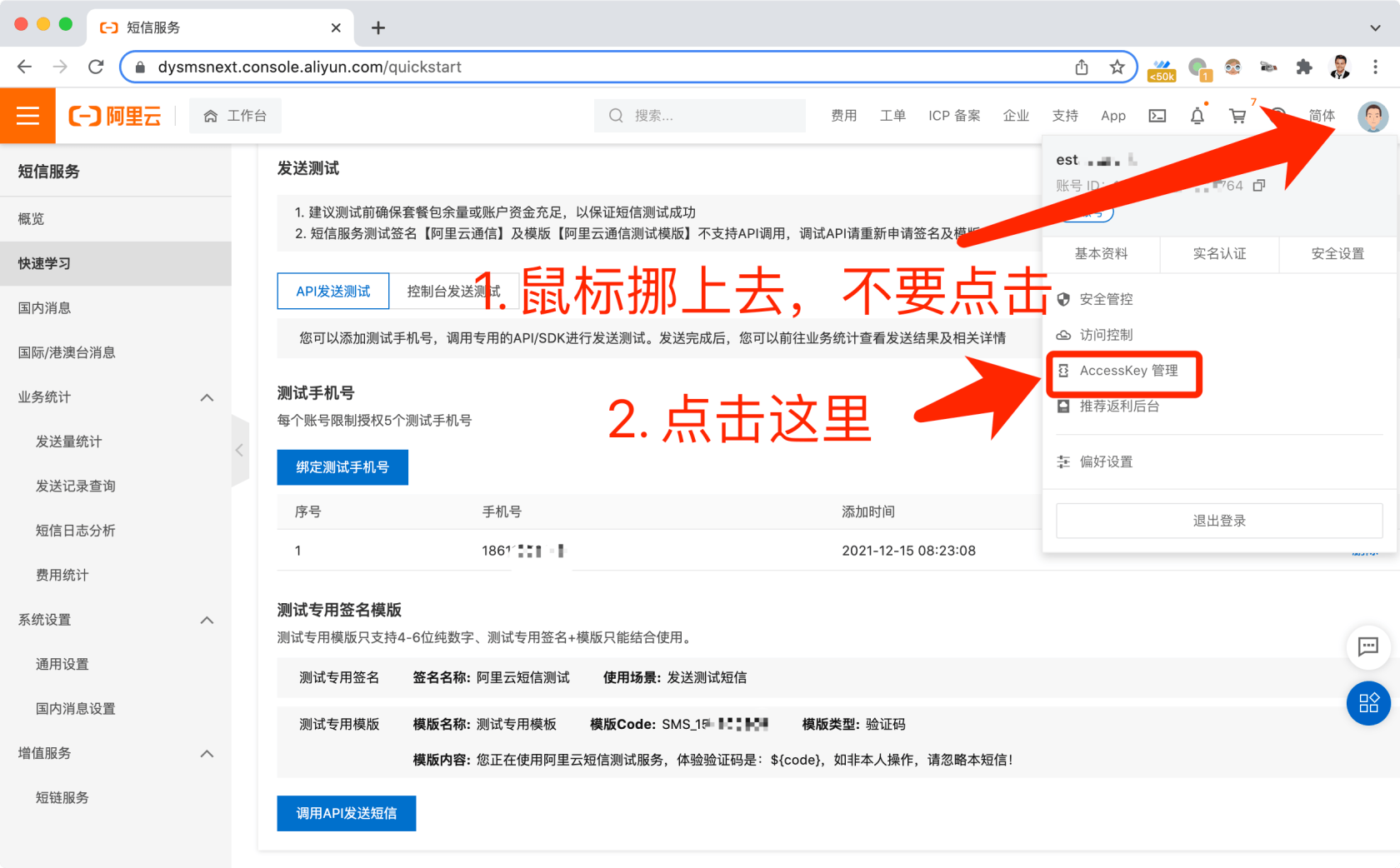
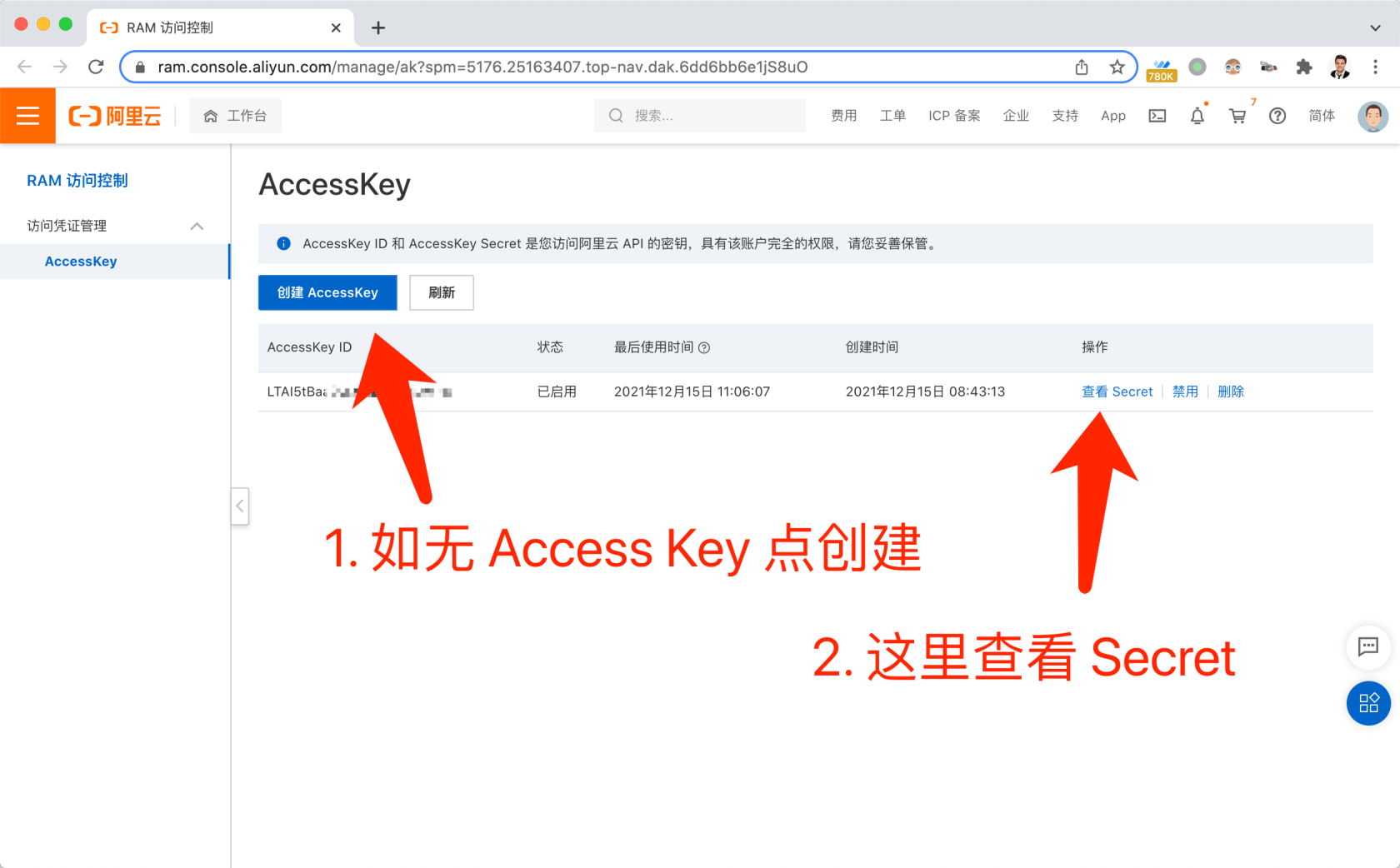
# 此外我们还需要在阿里云申请短信服务并且获取accesskey ID和accesskey secret
|
开始编码
封装sms
pkg/sms/driver_interface.go
1
2
3
4
5
| package sms
type Driver interface {
Send(phone string, message Message, config map[string]string) bool
}
|
pkg/sms/driver_aliyun.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| package sms
import (
"encoding/json"
aliyunsmsclient "github.com/KenmyZhang/aliyun-communicate"
"go-api-practice/pkg/logger"
)
type Aliyun struct{}
func (s *Aliyun) Send(phone string, message Message, config map[string]string) bool {
smsClient := aliyunsmsclient.New("http://dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com/")
templateParam, err := json.Marshal(message.Data)
if err != nil {
logger.ErrorString("Aliyun sms error", "json.Marshal error", err.Error())
return false
}
logger.DebugJSON("Aliyun sms", "config", config)
result, err := smsClient.Execute(
config["access_key_id"],
config["access_key_secret"],
phone,
config["sign_name"],
message.Template,
string(templateParam),
)
logger.DebugJSON("Aliyun sms", "request", smsClient.Request)
logger.DebugJSON("Aliyun sms", "result", result)
if err != nil {
logger.ErrorString("Aliyun sms error", "Execute error", err.Error())
return false
}
resultJSON, err := json.Marshal(result)
if err != nil {
logger.ErrorString("Aliyun sms error", "json.Marshal error", err.Error())
return false
}
if result.IsSuccessful() {
logger.DebugString("Aliyun sms", "success", "")
return true
} else {
logger.ErrorString("Aliyun sms", "error", string(resultJSON))
return false
}
}
|
pkg/sms/sms.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| package sms
import (
"go-api-practice/pkg/config"
"sync"
)
type Message struct {
Template string
Data map[string]string
Content string
}
type SMS struct {
Driver Driver
}
var once sync.Once
var internalSMS *SMS
func NewSMS() *SMS {
once.Do(func() {
internalSMS = &SMS{
Driver: &Aliyun{},
}
})
return internalSMS
}
func (sms *SMS) Send(phone string, message Message) bool {
return sms.Driver.Send(phone, message, config.GetStringMapString("sms.aliyun"))
}
|
我们先把阿里云的sms包封装成一个Send函数
验证手机验证码
在这里值得一提的是,我们要注意在整个用手机发送短信的过程中,有两个不同的验证码,由captcha生成的验证码和手机发送的验证码,这里我们先来完成验证手机验证码的逻辑
pkg/verifycode/store_interface.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| package verifycode
type Store interface {
Set(id string, value string) bool
Get(id string, clear bool) string
Verify(id, answer string, clear bool) bool
}
|
虽然是两个不同的验证码,但是处理逻辑是类似的,这里的接口和captcha中的Store实际上是一致的,接下来我们来实现这个接口
pkg/verifycode/store_redis.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| package verifycode
import (
"go-api-practice/pkg/app"
"go-api-practice/pkg/config"
"go-api-practice/pkg/redis"
"time"
)
type RedisStore struct {
RedisClient *redis.RedisClient
keyPrefix string
}
func (s *RedisStore) Set(key string, value string) bool {
ExpireTime := time.Minute * time.Duration(config.GetInt64("verifycode.expire_time"))
if app.IsLocal() {
ExpireTime = time.Minute * time.Duration(config.GetInt64("verifycode.debug.expire_time"))
}
return s.RedisClient.Set(s.keyPrefix+key, value, ExpireTime)
}
func (s *RedisStore) Get(key string, clear bool) (value string) {
key = s.keyPrefix + key
val := s.RedisClient.Get(key)
if clear {
s.RedisClient.Del(key)
}
return val
}
func (s *RedisStore) Verify(key string, answer string, clear bool) bool {
value := s.Get(key, clear)
return value == answer
}
|
可以发现与captcha中的逻辑基本一致,最后再把这些函数封装到一个功能完善的包中
pkg/verifycode/verifycode.go
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| package verifycode
import (
"go-api-practice/helpers"
"go-api-practice/pkg/app"
"go-api-practice/pkg/config"
"go-api-practice/pkg/logger"
"go-api-practice/pkg/redis"
"go-api-practice/pkg/sms"
"strings"
"sync"
)
type VerifyCode struct {
Store Store
}
var once sync.Once
var internalVerifyCode *VerifyCode
func NewVerifyCode() *VerifyCode {
once.Do(func() {
internalVerifyCode = &VerifyCode{
Store: &RedisStore{
RedisClient: redis.Redis,
keyPrefix: config.GetString("app.name") + ":verifycode:",
},
}
})
return internalVerifyCode
}
func (vc *VerifyCode) SendSMS(phone string) bool {
code := vc.generateVerifyCode(phone)
if !app.IsProduction() && strings.HasPrefix(phone, config.GetString("verifycode.debug_phone_prefix")) {
return true
}
return sms.NewSMS().Send(phone, sms.Message{
Template: config.GetString("sms.aliyun.template_code"),
Data: map[string]string{
"code": code,
},
})
}
func (vc *VerifyCode) CheckAnswer(key string, answer string) bool {
logger.DebugJSON("验证码", "检查验证码", map[string]string{key: answer})
if !app.IsProduction() &&
(strings.HasSuffix(key, config.GetString("verifycode.debug_email_suffix")) ||
strings.HasPrefix(key, config.GetString("verifycode.debug_phone_prefix"))) {
return true
}
return vc.Store.Verify(key, answer, false)
}
func (vc *VerifyCode) generateVerifyCode(key string) string {
code := helpers.RandomNumber(config.GetInt("verifycode.code_length"))
if app.IsLocal() {
code = config.GetString("verifycode.debug_code")
}
logger.DebugJSON("验证码", "生成验证码", map[string]string{key: code})
vc.Store.Set(key, code)
return code
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| if !app.IsProduction() &&
(strings.HasSuffix(key, config.GetString("verifycode.debug_email_suffix")) ||
strings.HasPrefix(key, config.GetString("verifycode.debug_phone_prefix"))) {
return true
}
|
与前面验证captcha类似,这里我们对于特殊的邮箱和手机号,我们直接放行
验证captcha验证码
刚刚我们已经提过了,我们除了验证手机验证码,还要验证captcha验证码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| package requests
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/thedevsaddam/govalidator"
"go-api-practice/pkg/captcha"
)
type VerifyCodePhoneRequest struct {
CaptchaID string `json:"captcha_id,omitempty" valid:"captcha_id"`
CaptchaAnswer string `json:"captcha_answer,omitempty" valid:"captcha_answer"`
Phone string `json:"phone,omitempty" valid:"phone"`
}
func VerifyCodePhone(data interface{}, c *gin.Context) map[string][]string {
rules := govalidator.MapData{
"captcha_id": []string{"required"},
"captcha_answer": []string{"required", "digits:6"},
"phone": []string{"required", "digits:11"},
}
messages := govalidator.MapData{
"captcha_id": []string{
"required:请输入验证码",
},
"captcha_answer": []string{
"required:请输入验证码",
"digits:验证码长度必须是6位",
},
"phone": []string{
"required:请输入手机号",
"digits:手机号长度必须是11位",
},
}
errs := validate(data, rules, messages)
_data := data.(*VerifyCodePhoneRequest)
if ok := captcha.NewCaptcha().VerifyCaptcha(_data.CaptchaID, _data.CaptchaAnswer); !ok {
errs["captcha_answer"] = append(errs["captcha_answer"], "验证码错误")
}
return errs
}
|
我们从前端接受验证码和手机号并且验证它们
完成控制器
在我们完成之前的工具包之后,控制器就变得简洁了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| func (vc *VerifyCodeController) SendUsingPhone(c *gin.Context) {
request := requests.VerifyCodePhoneRequest{}
if ok := requests.Validate(c, &request, requests.VerifyCodePhone); !ok {
return
}
if ok := verifycode.NewVerifyCode().SendSMS(request.Phone); !ok {
response.Abort500(c, "发送失败")
} else {
response.Success(c)
}
}
|
最后我们在路由中注册
1
2
3
| vcc := new(auth.VerifyCodeController)
authGroup.POST("/verify-codes/captcha", vcc.ShowCaptcha)
authGroup.POST("/verify-codes/phone", vcc.SendUsingPhone)
|
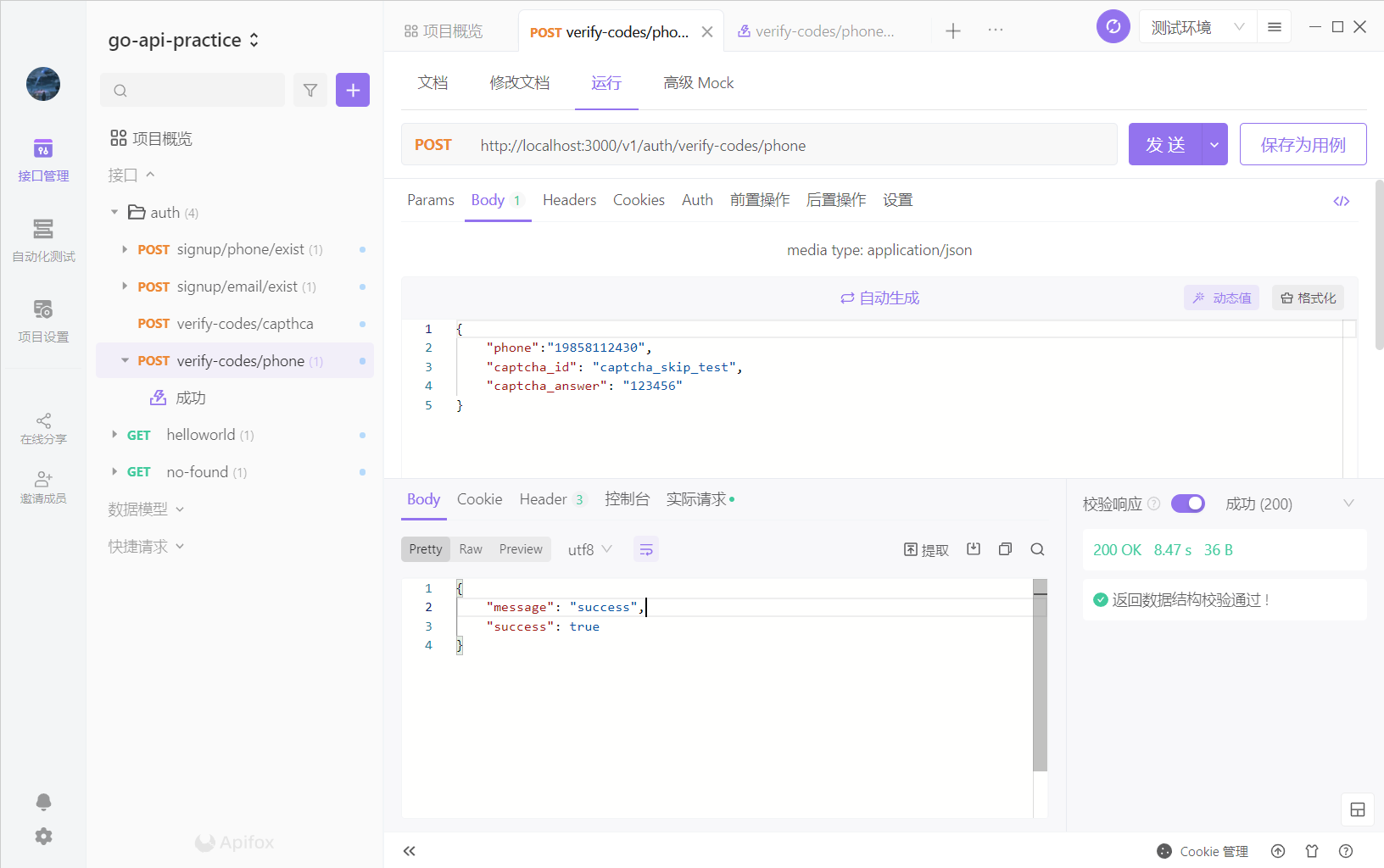
测试
我们在apifox中创建接口,看看短信能否发送成功
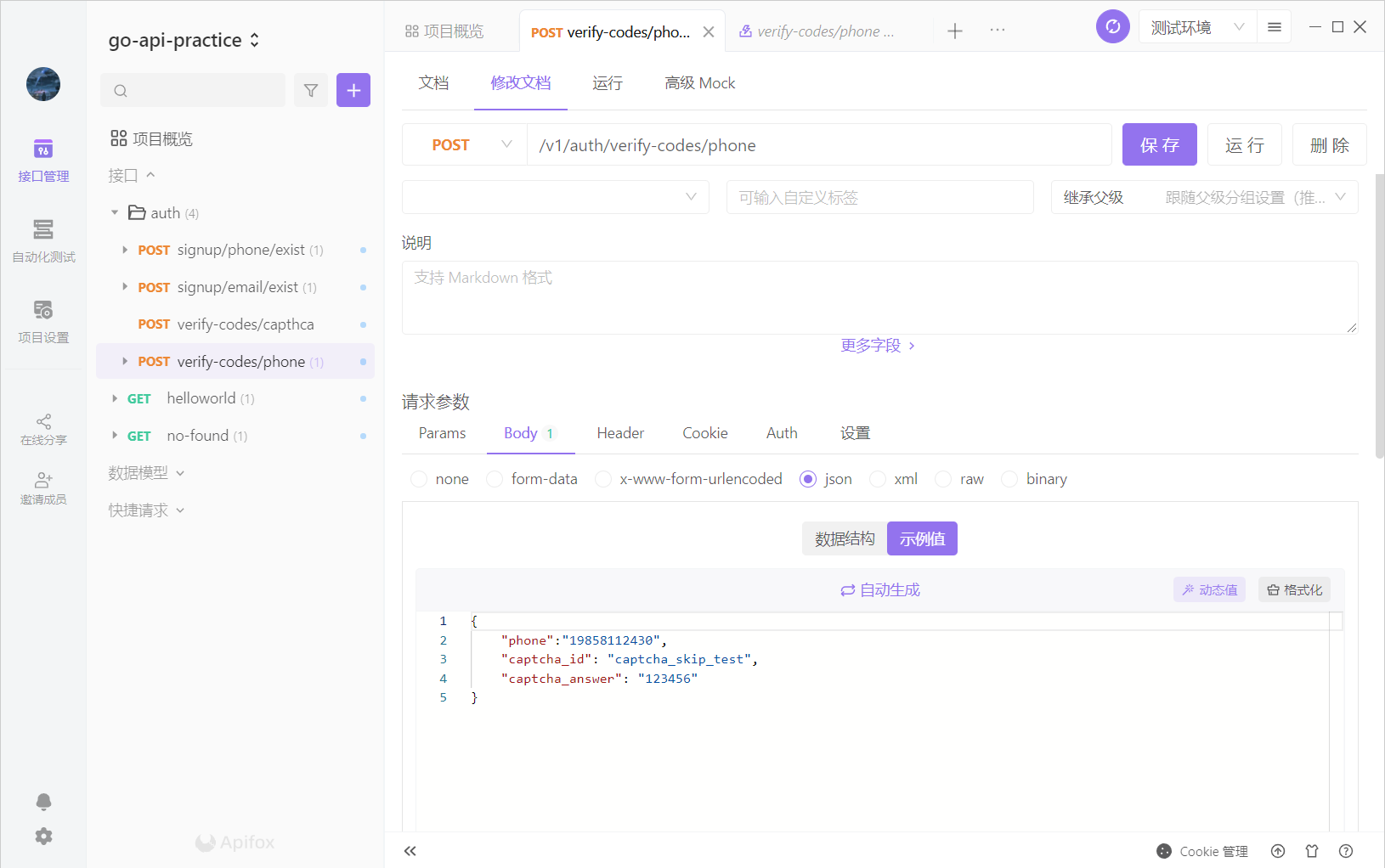
成功结果如下