AtCoder Beginner Contest 248
AtCoder Beginner Contest 248
下载PDF,获得别样的观看体验

A - Lacked Number
题意:
给出10个数字,输出0~9中未出现的那个数字。
思路:
统计数字出现情况即可。
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
B - Slimes
题意:
给定三个数字,每次操作可以使,输出的最小次数
思路:
直接模拟即可。
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
C - Dice Sum
题意:
现要求找到一个长度为的序列,对于其中的每一个元素,满足如下要求:
询问满足要求的序列个数。
思路:
考虑动态规划
设有:
- 第一维表示当前序列长度
- 第二维表示当前序列的和
- 数组的值表示方案数
枚举所有长度以及序列和,进行状态转移即可。
转移方程:
1 | for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) |
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
D - Range Count Query
题意:
给定一个长度为的序列,和个询问,询问格式如下:
给定,要求输出序列中到区间内值为$X的个数。
思路:
因为,所以我们可以用一个数组,把每一个数字的所有下标分别存起来,然后用二分解决询问即可。
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
E - K-colinear Line
题意:
在坐标平面内存在个点,每个点的坐标为,询问存在多少条不同的直线,穿过至少个点。
思路:
因为两点可以确定一条直线,而且点数,所以可以进行如下处理:
- 两两枚举所有的点
- 在确定完一条直线后,枚举所有的点判断这条直线穿过了多少点
三个点在一条直线上,显然有
将所有满足条件的直线统计出来即可。
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
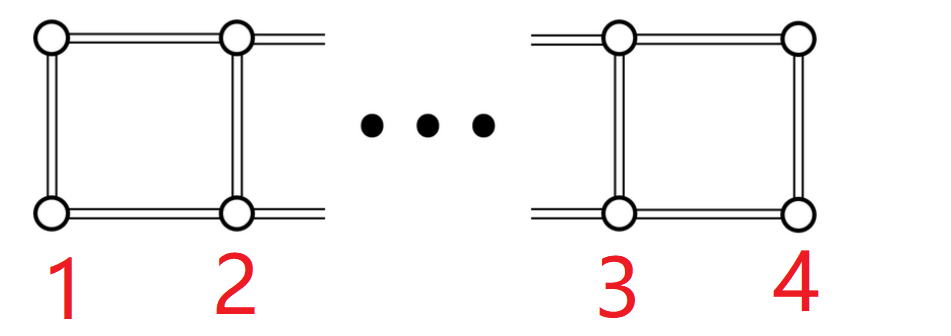
F - Keep Connect
题意:
给出这样的一个连通图,对于每一个,输出删除条边并且仍然保持连通性的方案数。
思路:
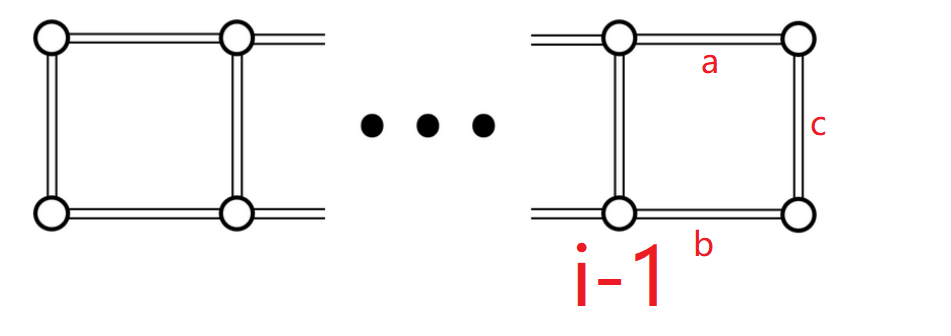
考虑动态规划
设有:
- 表示前组点
- 表示删除的边数
- 第三维记录的是第组点之间的连通性(第组的两个点当前能否连通)
- 数组值表示方案数
我们用三个值来代表三条边,表示这条边是否删除。
- 那么当第组点是不连通的时候,显然是要保证两条边都相连,否则整张图必然失去连通性。
- 当第组点是连通的时候,我们只需要保证有一条边是连通的即可,如果三边中相连了至少两条边,那么就可以保证第组点是连通的。
有转移方程
1 | if(!k) |
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
Ex - Beautiful Subsequences
题意:
给定一个长度为的全排列,询问满足如下条件的区间个数:
思路:
线段树+单调栈:
- 线段树:我们先固定一个,然后尝试去维护一个序列,这个序列中的第个点记录的值为,如果这个值,那么这个点所代表的区间就是一个合法区间,此外,因为这个序列是全排列,所以不难发现不会是负数。我们用线段树去维护这一段区间,区间内记录的最小值,并且记录下的点的个数。
然后就可以通过根节点的信息推知答案。- 单调栈:我们可以通过单调栈动态的确定区间最值,确定完最值以后通过线段树区间修改即可。
时间复杂度:
AC代码:

1 |
|
此外,大家也可以看dls的视频讲解,在这里附上链接
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 jking の 博客!